See how technology is revolutionizing agriculture with these eighteen innovations. Explore how tech enhances crop yields and sustainability, from smart farming techniques to automated machinery. Agriculture is embracing technology to meet the demands of a growing population and climate challenges. Here are 16 tech innovations transforming the agricultural sector. From precision farming and drone technology to automated machinery, learn how these advancements improve crop yields and promote sustainability.
Precision Farming

Precision farming uses GPS technology and data analytics to manage fields with high accuracy. Farmers can monitor soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns, allowing them to make informed decisions about planting and harvesting. This method reduces waste and optimizes the use of resources such as water and fertilizers.
Precision farming also helps in identifying pest and disease outbreaks early, enabling timely intervention. By tailoring treatments to specific areas of a field, farmers can reduce the environmental impact and improve crop yields. Overall, precision farming leads to more sustainable and efficient agricultural practices.
Drones
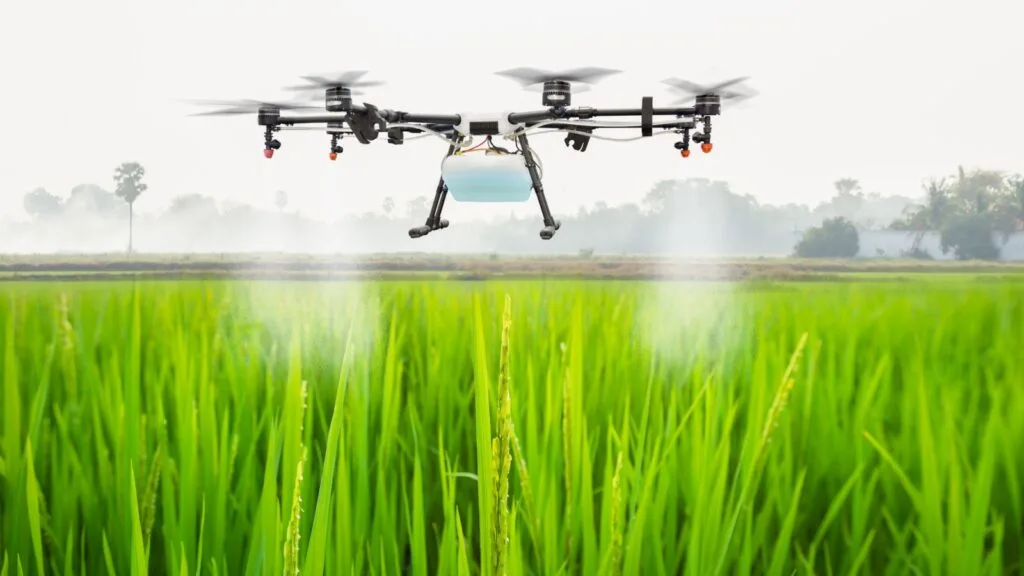

Drones are revolutionizing how farmers monitor their crops and land. Equipped with cameras and sensors, drones can quickly survey large areas, capturing detailed images that highlight issues such as pest infestations, water stress, and nutrient deficiencies. This aerial perspective provides valuable data that can be used to address problems before they become severe.
In addition to monitoring, drones are also used for tasks such as planting seeds and spraying pesticides. This automation reduces labor costs and increases efficiency. The precise application of treatments also minimizes the use of chemicals, promoting a healthier environment.
Automated Machinery
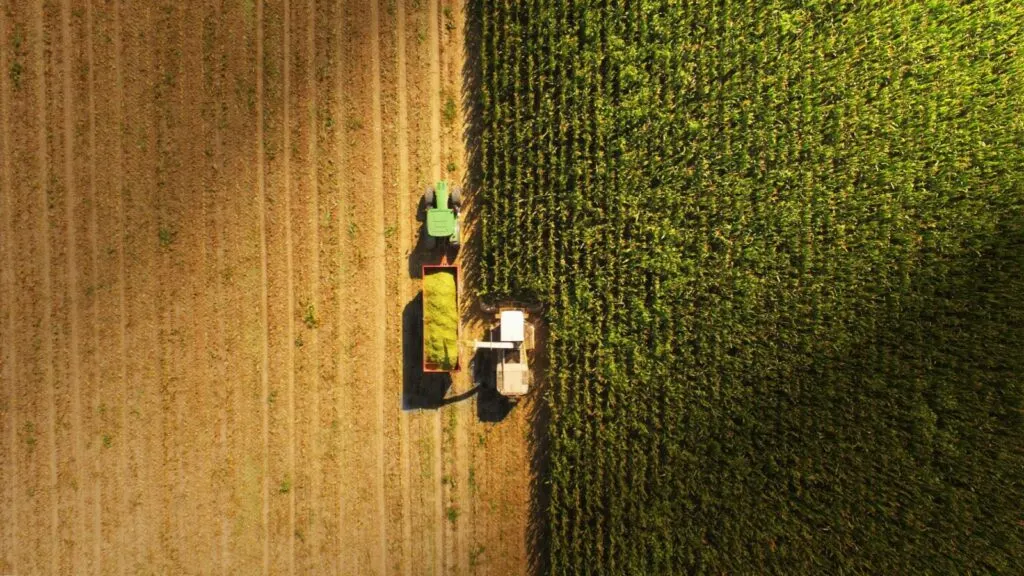

Automated machinery, including tractors and harvesters, is transforming traditional farming operations. These machines can operate independently, performing tasks like planting, watering, and harvesting with minimal human intervention. This technology increases productivity and reduces the need for manual labor, addressing the issue of labor shortages in agriculture.
Automation also allows for more consistent and precise farming practices. Machines can work around the clock, ensuring that tasks are completed promptly. As a result, farmers can achieve higher yields and better-quality produce.
IoT Sensors

The Internet of Things (IoT) is making farms smarter with the use of interconnected sensors. These sensors monitor various parameters such as soil moisture, bug detector, temperature, and humidity in real-time. The data collected helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and crop protection.
IoT sensors can also alert farmers to potential problems, such as equipment malfunctions or adverse weather conditions. This early warning system allows for prompt action, reducing the risk of crop loss. Overall, IoT technology enhances farm management and operational efficiency.
Vertical Farming

Vertical farming involves growing crops in stacked layers, often in controlled indoor environments. This method maximizes space usage and allows for year-round production, independent of external weather conditions. By controlling factors such as light, temperature, and humidity, vertical farms can achieve optimal growing conditions.
Vertical farming also uses less water and land compared to traditional farming. This sustainable approach reduces the need for pesticides and herbicides, resulting in cleaner produce. Moreover, it brings food production closer to urban areas, reducing transportation costs and carbon emissions.
Biotechnology

Biotechnology is playing a crucial role in developing crops that are more resilient to environmental stresses. Through genetic modification, scientists can create plants that are resistant to pests, diseases, and extreme weather conditions. This innovation helps ensure food security in the face of climate change.
Additionally, biotechnology can enhance the nutritional content of crops. For example, biofortified crops contain higher levels of essential vitamins and minerals, addressing malnutrition issues. Biotechnology offers the potential for higher yields and healthier food.
Blockchain Technology

Blockchain technology is improving transparency and traceability in the agricultural supply chain. Recording transactions on a secure and immutable ledger ensures that all parties involved can track the journey of produce from farm to table. This traceability helps in verifying the authenticity and quality of agricultural products.
Blockchain can streamline administrative processes such as contracts and payments. It reduces the risk of fraud and enhances trust between farmers, suppliers, and consumers. The technology promotes a more efficient and accountable agricultural industry.
Artificial Intelligence

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is being used to analyze large datasets and provide actionable insights for farmers. AI-powered tools can predict weather patterns, optimize irrigation schedules, and identify potential issues before they become critical. This data-driven approach enhances decision-making and improves farm management.
AI is also being used in precision agriculture to monitor crop health and yield. Machine learning algorithms can process images from drones and sensors to detect anomalies and suggest corrective actions. The integration of AI in agriculture leads to smarter and more efficient farming practices.
Hydroponics
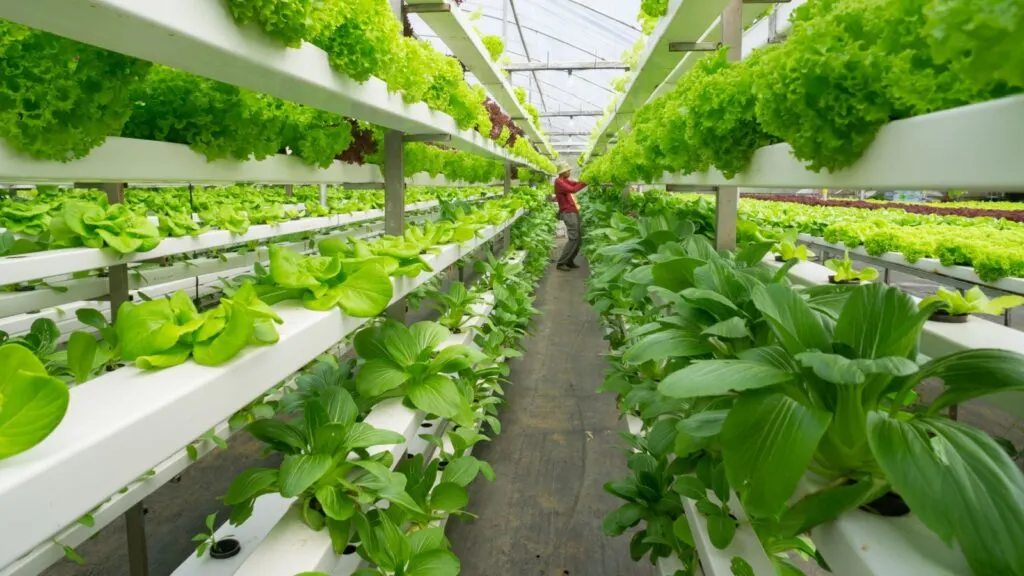

Hydroponics is a soil-less method of growing plants using nutrient-rich water solutions. This technique allows for precise control over the nutrients that plants receive, leading to faster growth and higher yields. Hydroponics also uses significantly less water compared to traditional farming.
This method can be practiced indoors or in greenhouses, making it suitable for urban environments and areas with poor soil quality. By reducing the dependence on soil, hydroponics minimizes the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests. It offers a sustainable and efficient way to produce fresh produce year-round.
Genomic Editing
Genomic editing technologies, such as CRISPR, allow scientists to make precise changes to the DNA of crops. This can result in plants that are more resistant to diseases, pests, and environmental stresses. Genomic editing holds the potential to enhance crop yields and improve food security.
Furthermore, this technology can be used to develop crops with improved nutritional profiles. For example, scientists can create varieties with higher vitamin content or better flavor. Genomic editing represents a significant advancement in agricultural biotechnology.
Mobile Applications

Mobile applications are providing farmers with easy access to information and tools that enhance their productivity. From weather forecasts and market prices to pest identification and crop management advice, these apps offer valuable resources at farmers’ fingertips. This accessibility empowers farmers to make better-informed decisions.
Mobile apps also facilitate communication and knowledge sharing among farming communities. Farmers can connect with experts, share experiences, and access training materials through these platforms. The use of mobile technology is bridging the information gap in agriculture.
Remote Sensing

Remote sensing technology uses satellites and aerial imagery to monitor agricultural land. It provides valuable data on soil conditions, crop health, and environmental factors. This information helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
Remote sensing also enables early detection of issues such as drought, disease outbreaks, and nutrient deficiencies. By identifying problems early, farmers can take corrective actions to minimize crop loss. This technology enhances the overall management and productivity of farms.
Climate-Smart Agriculture

Climate-smart agriculture involves practices and technologies that help farmers adapt to and mitigate the impacts of climate change. This includes techniques such as conservation tillage, cover cropping, and agroforestry. These practices improve soil health, increase biodiversity, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Incorporating climate-smart technologies, such as weather forecasting tools and drought-resistant crops, also helps farmers manage climate risks. By adopting sustainable practices, farmers can enhance resilience and ensure long-term productivity. Climate-smart agriculture promotes a more sustainable and adaptive farming system.
Solar-Powered Technology
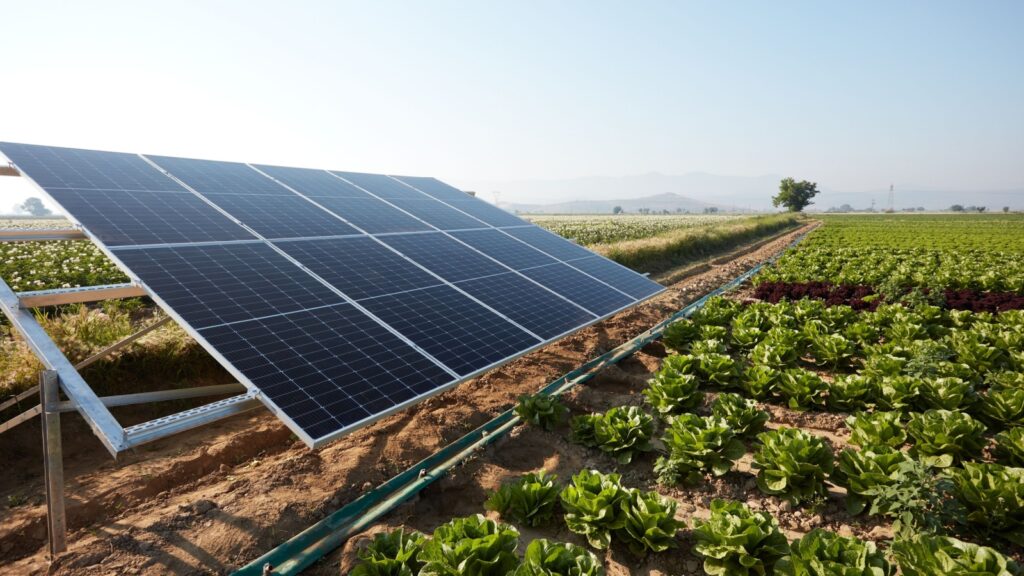

Solar-powered technology is providing renewable energy solutions for farms. Solar panels can power irrigation systems, greenhouses, and other farm equipment, reducing dependence on fossil fuels. This shift to renewable energy sources lowers operational costs and decreases the carbon footprint of agriculture.
Solar-powered technology also enables off-grid farming, providing energy access to remote and rural areas. This promotes sustainable development and energy independence for farmers. The integration of solar power in agriculture supports environmental conservation and economic viability.
Aquaponics
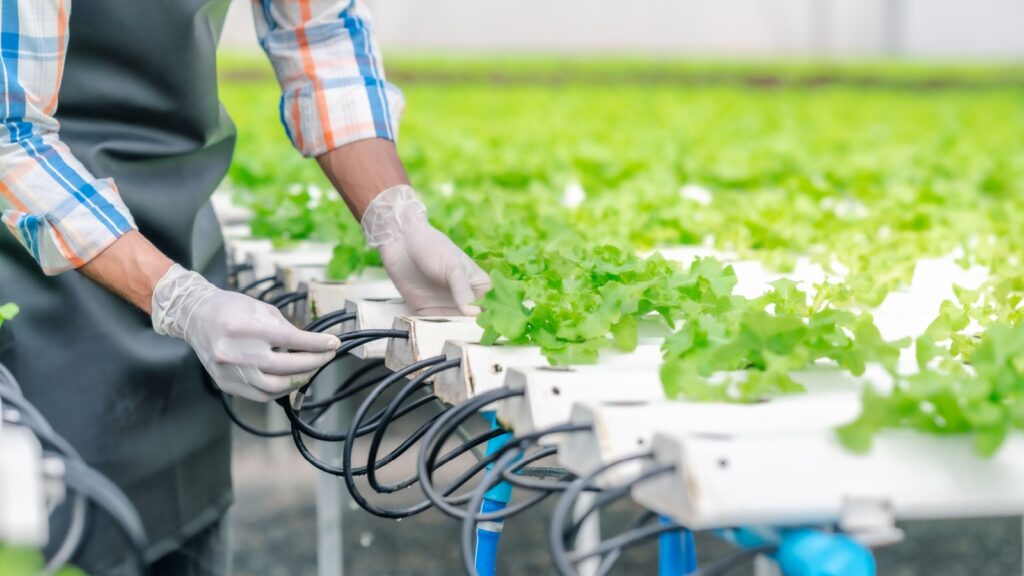

Aquaponics combines aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil) in a symbiotic environment. The waste produced by fish provides nutrients for plants, while the plants help to filter and clean the water. This closed-loop system conserves water and produces both fish and vegetables.
Aquaponics can be practiced in various settings, including urban environments and areas with limited arable land. It offers a sustainable and efficient way to produce food, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Aquaponics represents an innovative approach to integrated farming.
Agricultural Robots
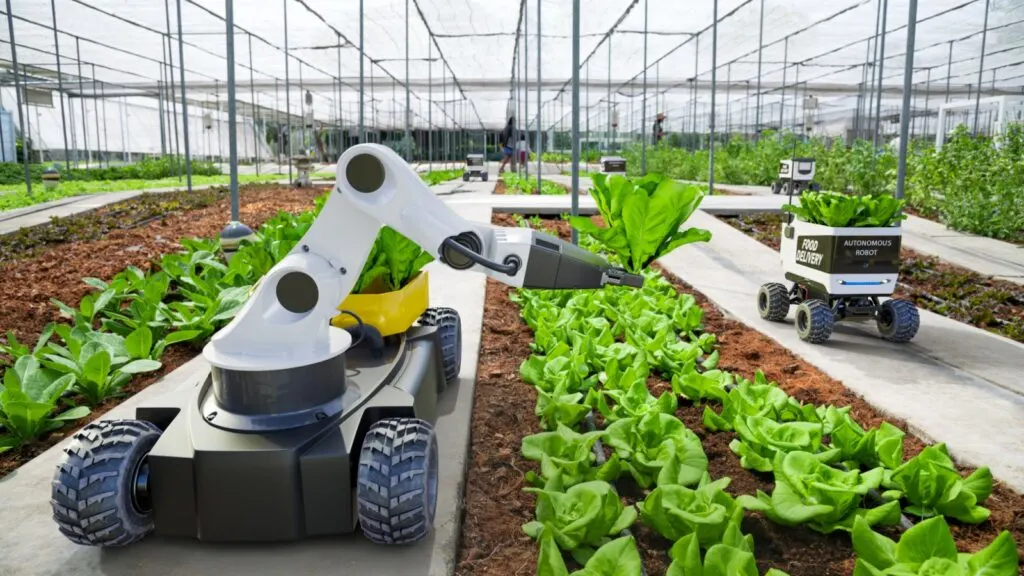

Agricultural robots are designed to perform specific tasks such as weeding, pruning, and harvesting. These robots can operate autonomously or under human supervision, increasing efficiency and precision in farming operations. They help reduce labor costs and improve productivity.
The use of robots in agriculture also enhances the accuracy of tasks, such as applying fertilizers and pesticides and minimizing waste and environmental impact. As technology advances, agricultural robots are becoming more versatile and accessible to farmers. This innovation is driving the future of smart farming.
