3D printing technology is making significant strides in the medical field, offering revolutionary solutions for complex challenges. From custom prosthetics to bioprinting organs, 3D printing is changing the face of medicine. See how this cutting-edge technology is saving lives and improving healthcare outcomes. Check out the latest advancements in medical 3D printing and their impact on patient care. Here are groundbreaking uses of 3D printing in medicine, and its potential to transform healthcare as we know it.
Custom Prosthetics

3D printing has revolutionized the creation of prosthetics, allowing for custom designs tailored to individual patients. This technology enables the production of prosthetics that fit perfectly, providing better comfort and functionality. It also significantly reduces the cost and time required to produce these devices, making them more accessible to those in need.
Custom prosthetics also offer a higher level of personalization, with the ability to design aesthetic features that match the patient’s skin tone and personal preferences. This has led to increased patient satisfaction and improved psychological well-being. The precision and adaptability of 3D printing make it an ideal solution for children who quickly outgrow traditional prosthetics.
Bioprinting Organs
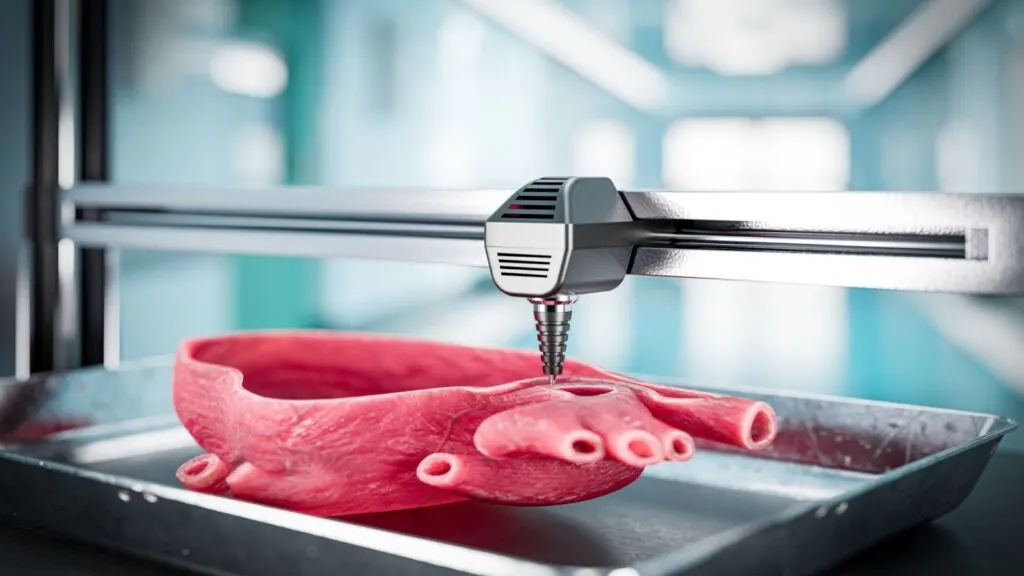

One of the most groundbreaking uses of 3D printing in medicine is bioprinting, the creation of organ and tissue structures using living cells. This technology holds the potential to address the critical shortage of donor organs. By using a patient’s own cells, bioprinting can create organs that are less likely to be rejected by the immune system.
Bioprinting also allows for the testing of new drugs and treatments on human-like tissues, improving the safety and efficacy of medical research. While still in its early stages, the promise of bioprinting organs could transform transplantation and regenerative medicine, offering hope to thousands of patients worldwide.
Surgical Planning And Training
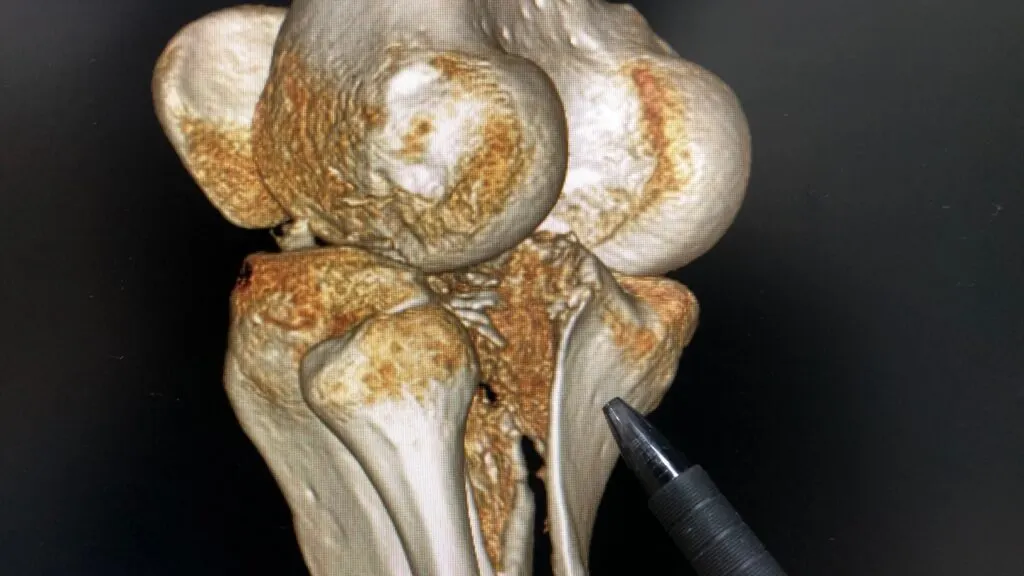
3D printing enhances surgical planning and training by providing accurate anatomical models based on patient imaging data. Surgeons can practice complex procedures on these models before performing them on actual patients, leading to better outcomes. This approach reduces the risk of complications and shortens surgery times.
Medical students and residents also benefit from these realistic models, gaining hands-on experience in a controlled environment. This advanced training method helps to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills, ultimately improving the quality of healthcare.
Customized Implants
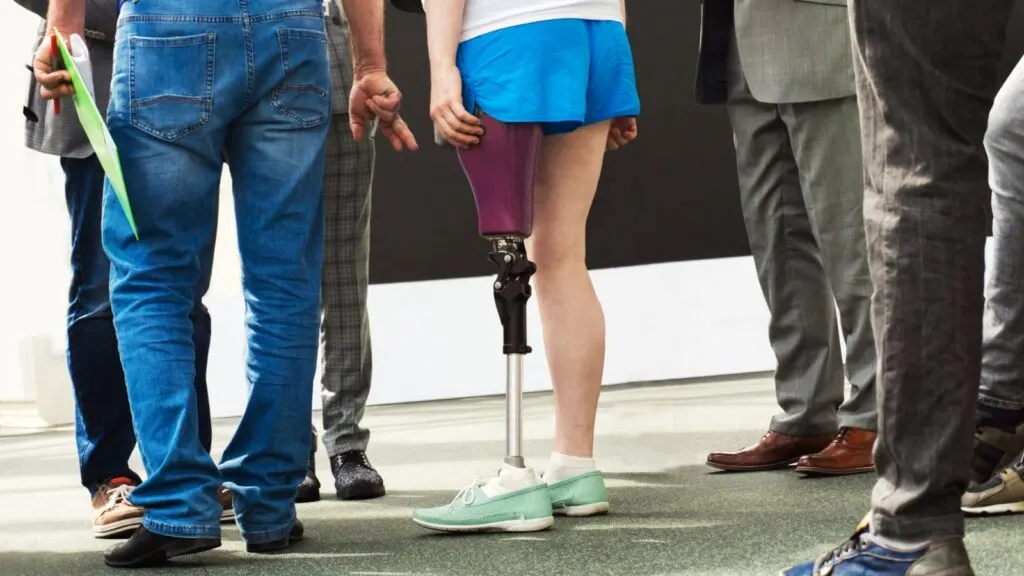
The ability to create customized implants is another significant advantage of 3D printing in medicine. Traditional implants often require adjustments during surgery to fit the patient’s anatomy, but 3D printing allows for the creation of implants that match the exact specifications needed. This results in better integration with the patient’s body and faster recovery times.
Customized implants are particularly beneficial in cases involving complex bone structures, such as cranial or spinal surgeries. The precision of 3D printing ensures a perfect fit, enhancing the overall success of the surgical procedure.
Orthopedic Solutions
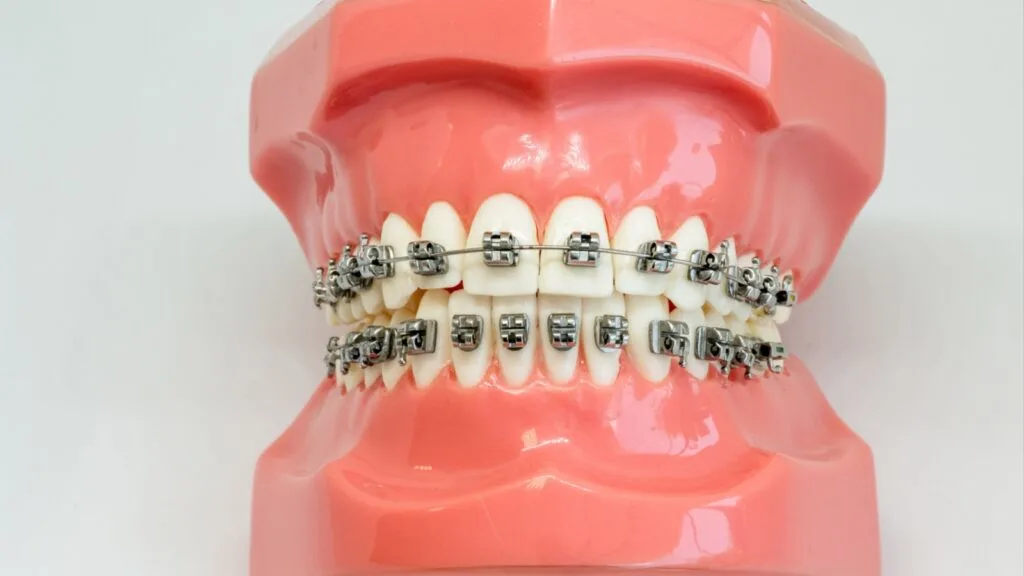
3D printing is transforming orthopedic care by enabling the production of personalized orthopedic devices and surgical tools. Custom casts, braces, and splints made from 3D printing technology offer better comfort and support compared to traditional options. These devices can be designed to fit the unique contours of a patient’s body, promoting quicker healing.
3D printing also allows for the rapid production of surgical guides and instruments tailored to individual surgeries. This precision reduces the margin for error during orthopedic procedures, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced recovery times.
Dental Applications
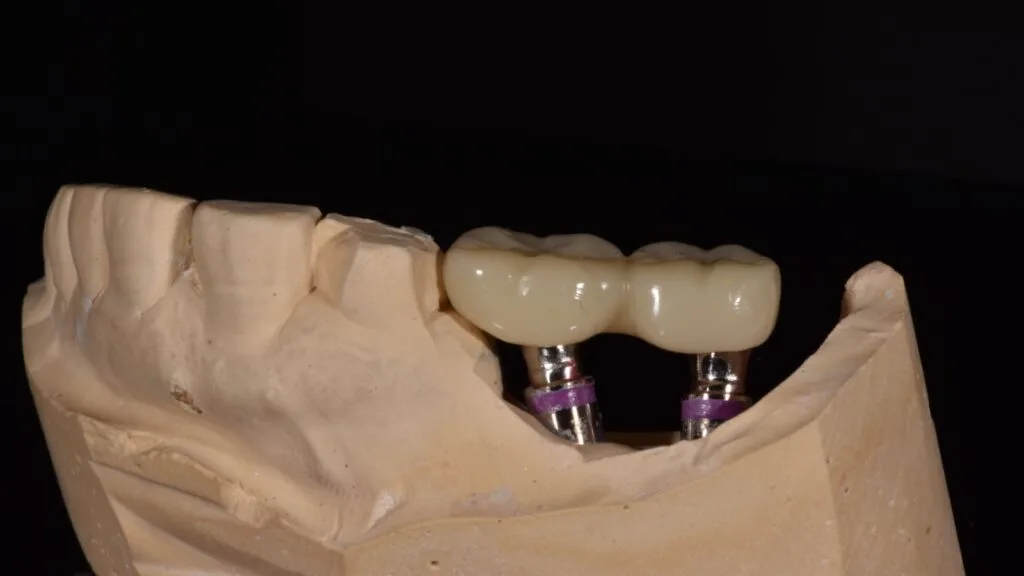
In dentistry, 3D printing is being used to create custom crowns, bridges, dentures, and orthodontic devices with remarkable accuracy. This technology allows for faster production and more precise fittings, improving patient comfort and satisfaction. Digital impressions eliminate the need for uncomfortable molds, streamlining the process.
3D printing also facilitates the creation of surgical guides for dental implants, ensuring optimal placement and alignment. These advancements in dental applications are not only enhancing the quality of care but also making dental treatments more efficient and less invasive.
Hearing Aids
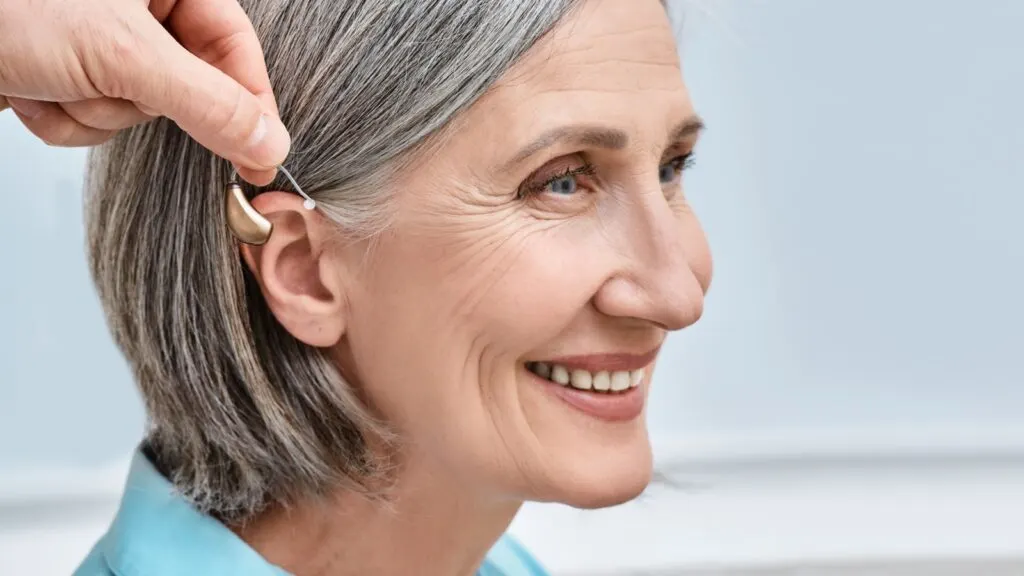
The production of hearing aids has been revolutionized by 3D printing, allowing for rapid and precise customization. Each hearing aid can be tailored to fit the unique shape of a patient’s ear, enhancing comfort and effectiveness. This personalization leads to better sound quality and a more natural listening experience.
Fortunately, 3D printing has significantly reduced the time and cost associated with producing hearing aids. This has made high-quality, custom-fit hearing aids more accessible to individuals with hearing impairments, improving their overall quality of life.
Skin Grafts And Tissue Engineering
3D printing is being used to create skin grafts for burn victims and patients with severe wounds. By layering cells to form tissue, this technology can produce skin that is biologically compatible with the patient. This approach reduces the risk of rejection and promotes faster healing.
Tissue engineering with 3D printing also extends to the creation of other types of tissues, such as cartilage and blood vessels. These advancements are paving the way for more effective treatments for a variety of injuries and conditions, offering new hope for patients.
Pharmaceutical Research And Development

3D printing is playing a crucial role in pharmaceutical research by enabling the creation of custom drug delivery systems. This technology allows for the production of pills with precise dosages and release mechanisms tailored to individual patients. Personalized medicine is becoming a reality, improving treatment efficacy and patient compliance.
Researchers are also using 3D printing to create complex drug formulations and innovative delivery devices. This capability accelerates the development of new medications and enhances the ability to test their effectiveness in controlled, reproducible ways.
Organ Transplant Models
Before performing organ transplants, surgeons can use 3D-printed models to plan and practice the procedure. These models, based on the patient’s actual anatomy, provide a detailed representation of the organ and surrounding tissues. This preparation helps surgeons anticipate challenges and refine their techniques, leading to better surgical outcomes.
The use of 3D-printed models also facilitates communication within the surgical team and with patients, improving understanding and decision-making. This innovation is enhancing the success rates of complex transplant surgeries and reducing the risk of complications.
Bone Reconstruction
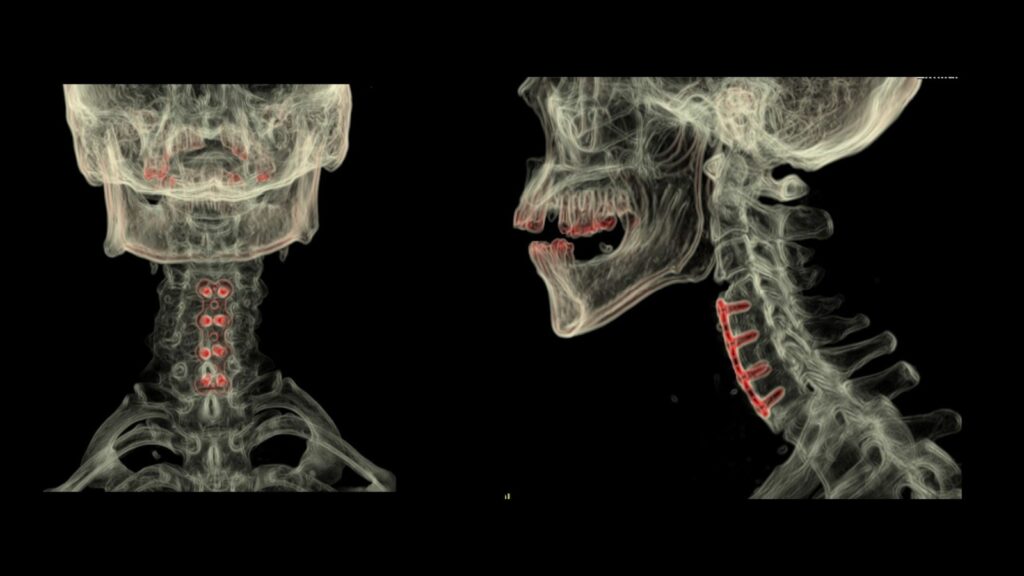
3D printing is making significant strides in the field of bone reconstruction. Customized bone grafts and implants can be created to match the patient’s unique anatomy, ensuring a perfect fit. This precision is particularly important for complex reconstructive surgeries, such as those involving the skull or jaw.
The use of 3D-printed bone substitutes also reduces the need for donor bone, minimizing the risk of infection and other complications. These advancements are improving patient outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for individuals undergoing reconstructive surgery.
Medical Device Prototyping

The development of new medical devices has been accelerated by 3D printing technology. Rapid prototyping allows engineers and designers to quickly create and test new device designs, iterating based on feedback and performance. This process significantly reduces the time and cost associated with bringing new medical devices to market.
3D printing also enables the customization of medical devices to meet the specific needs of patients and healthcare providers. This flexibility is driving innovation in the medical device industry, leading to the creation of more effective and user-friendly products.
Anatomical Models For Education
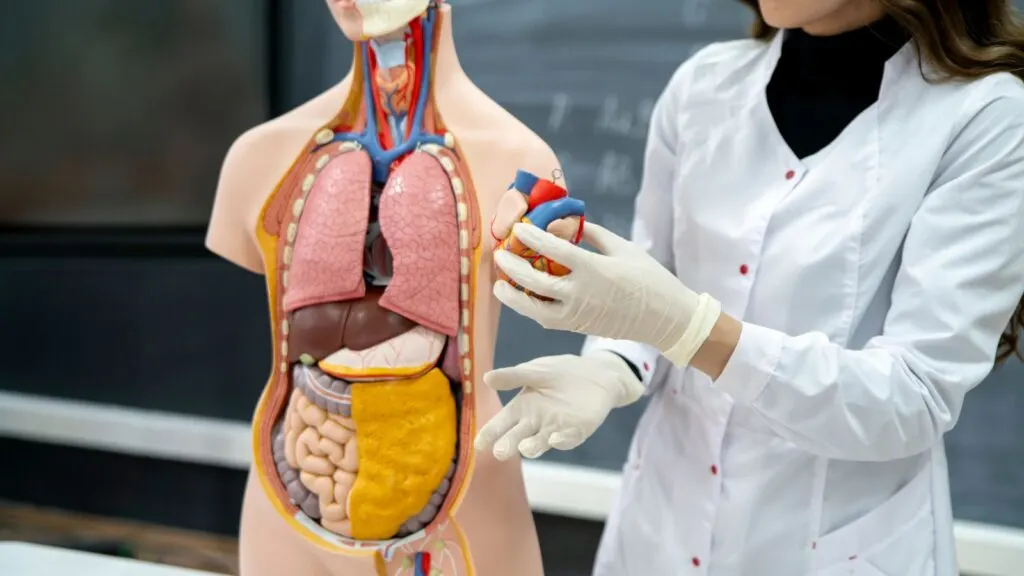
Medical education is being transformed by the use of 3D-printed anatomical models. These models provide a hands-on learning experience for students and professionals, enhancing their understanding of complex anatomical structures. The ability to study and interact with accurate replicas of human organs and tissues is invaluable in medical training.
These models are also used in patient education, helping individuals understand their conditions and the planned procedures. This improved communication fosters better patient engagement and compliance with treatment plans.
Surgical Implants And Meshes
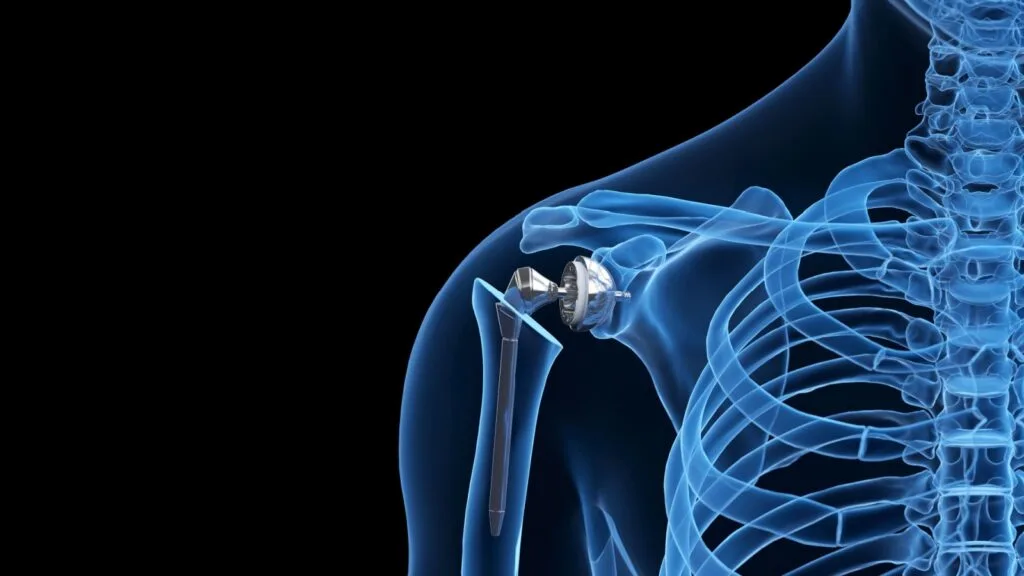
3D printing is being used to create surgical implants and meshes with precise specifications. These custom-made devices provide better integration with the patient’s body and reduce the risk of complications. For example, hernia meshes and spinal implants can be designed to match the exact needs of the patient, enhancing the success of the surgery.
The precision and customization offered by 3D printing also mean that these implants can be produced quickly and efficiently. This reduces waiting times for patients and allows for more timely interventions, improving overall healthcare outcomes.
Regenerative Medicine
In regenerative medicine, 3D printing is being used to create scaffolds that support the growth of new tissues and organs. These scaffolds provide a framework for cells to grow and develop, eventually forming functional tissue. This approach can potentially repair or replace damaged tissues, offering new treatment options for conditions with limited solutions.
The ability to create customized scaffolds that match the patient’s anatomy enhances the effectiveness of regenerative treatments. This innovation paves the way for breakthroughs in treating injuries and degenerative diseases.
Medical Instruments And Tools
Custom surgical instruments can be designed and produced quickly, tailored to the specific needs of the procedure and the surgeon’s preferences. This customization improves the precision and efficiency of surgeries.
3D printing also allows for the creation of complex tools that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods. This capability is driving innovation in surgical techniques and expanding the possibilities for minimally invasive procedures.
